Nepal yarn manufacturers’ association – UKaid Skill Development leading to employment / Public Private Partnership Program
Skills for employment program together with NYMA is a shared common interest in boosting skills of the workforce and improving the training and human resource management system at the factories to enable productivity and growth of the industry. The participants are enrolled in employment linked apprenticeship training model, in partnership with UKAID SEP.
partners
Scope for placement
Jobs Created
Ongoing Trainings

Who are the beneficiaries?
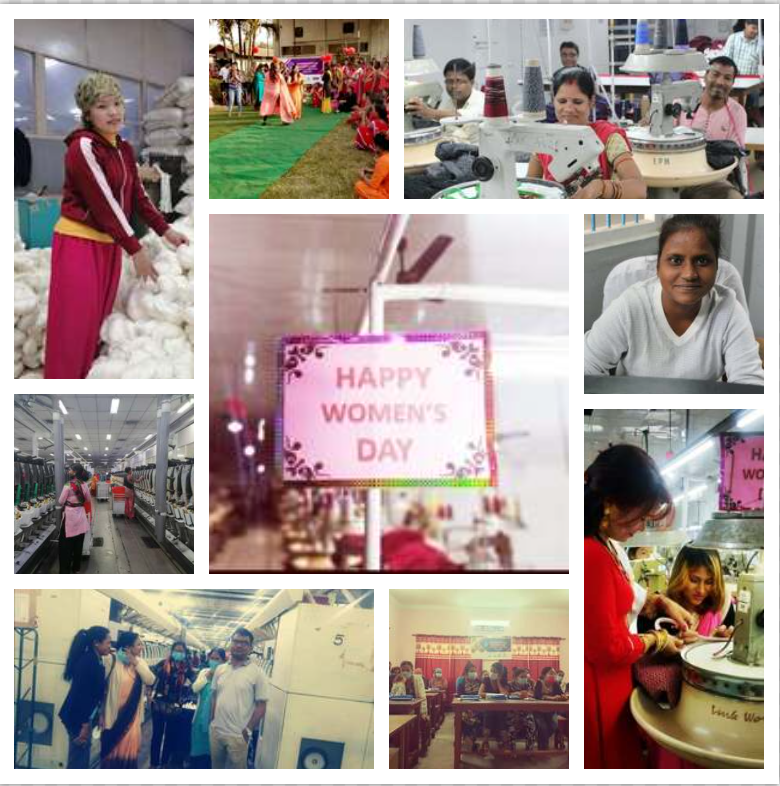
For job seekers, especially those from marginalized communities (eg Women, Disadvantaged groups and people with disabilities), this partnership has the potential increase in access to quality training, decent work, Government stipulated income, support retention and optimize workforce productivity levels.

Benefits
This partnership focuses on the yarn to the Garment value chain, with a special focus on but not limited to yarn industries. The participants will seek to leverage the UKaid Skills for Employment Programme’s challenge fund, to access co-investment and technical assistance, for piloting the apprenticeship programme in various job roles in demand, and fulfil the skills gap in the yarn to garment industries.
UKaid SEP Background
The Ukaid Funded four year SEP programme supports the generation of new employment and migration management by working with the government, employers in the private sector, training and education institutions, financial and remittance firms and recruitment agencies to pilot and scale innovative initiatives in priority sectors: tourism, commercial agriculture , construction (hydropower) and light manufacturing. Drawing on national and international resources, SEP provides co- investment and technical advisory support to partner with the private and public sector- using a Challenge Fund Mechanism- on efforts that introduce and expand sustainable training, employment and migration management models.

Why with NYMA?
NYMA member industries together, export 11 billion annually making Yarn Nepal’s largest export commodity; products go to India, Turkey and Europe. The industry expects production to double next year (from 40,000 ton currently to 80,000 ton). This in turn will require an estimated 5,000 additional workers by end of 2020. Industry leaders believe that 500,000 jobs can be created in Nepal over the next five years in the textile industry, comprising of the yarn to garment value chain from spinning, weaving, knitting, hosiery and garments.

Current Challenges
Finding skilled Nepali workers especially mill operators, spinners, weavers and supervisors is a persistent challenge for the factories; about 30% of the workforce comes from across the border. Similarly, high turnover of workers is another challenge- every month about 150-300 people on average per day factory which warrants 300-400 new replacements on a rolling monthly basis just to keep ahead of the turnover and optimize production.

Shared Goals, Potential areas of Collaboration and roles and responsibilities
Given the job growth potential of the yarn to garment industry value chain, the participants are interested in building sustainable and impact focused collaboration between the public and private organizations based on principles of shared interest and shared value- utilizing the strengths of each partner- to reach and empower 4,000 job seekers with quality, employment linked apprenticeship training over the next one year and spur growth of the factories. In the process, the participants seek to improve and expand the training capabilities of the factories and demonstrate replicable PPP model on apprenticeship training that can be adopted by other firms in the yarn to Garment Value chain and taken to scale up. This partnership has the potential to train and employ at least 10,000 people by 2022.
Objectives
Skills for employment program together with NYMA is a share common interest in boosting skills of the workforce
1
Assess the existing training infrastructure of its 4 partner industries, including training process mapping, delivery approaches, existing trainers’ capacity, curricula used by the partner industries, etc.
2
Enhancement at each of the partner NYMA factories in terms of trainee mobilization and screening strategy, training infrastructure, training delivery process, standard curriculum for each of identified job roles and training of trainers for individual partner industries collectively and specifically.
3
Application of PPP model on apprenticeship training adopted by the partner industries leading skills development to employment.
4
Co-develop/ revise and standardize training curriculum and methodology, curriculum to encompass soft skills in addition to technical skills.
5
Up skill Trainers and Mangers Assurance of training conducted by partner industries to up skill trainers at the factories for delivery of stronger technical and soft skills for new workers. Organize training for factory owners, managers and supervisors on good human resource management practices and leadership to build and boost conducive work environment for worker retention, growth and productivity.
6
Skilling of new trainees, conducting 1-6 months systematic regular training for trainees. Provision of transportation cost necessary safeguard and special consideration to encourage participation and retention of women (eg accommodation and child – care support).
7
Ensure smooth transition to jobs with formal contract for successful training graduates. Following is the job creation prospects per factory by August, 2020.
- Reliance Spinning Mills: 2002
- Triveni Spinning Mills: 1001
- Jagdamba Spinning Mills: 504
- Tricot Knitting Industries:270

Why is the project required at this time and location?
There is a huge turnover of human resources in particular to material handling and machine operation in yarn industries. The workers are mostly from across the border and seasonal.
The initiative will enable apprentice training leading to employment for at least 4,000 workers in the four factories associated with NYMA, of which 50% will be women and 70% will be disadvantaged groups (DAG).
To reach the aspirational production levels, the factories associated with NYMA need an additional 5,000 workers for the yarn industry alone by 2020 and an estimated 10,000 in total by three years. This is however an industry that sees high turnover, primarily due to the following reasons and therefore requiring constant churning on training and recruitment.
- Seasonal work for people from border
- Wage below market average
- Poor working conditions
- Skill building focusing on hard skills and not soft skills
- Inadequate HRM practices.
Partner Organizations






